Rachel Powers Research
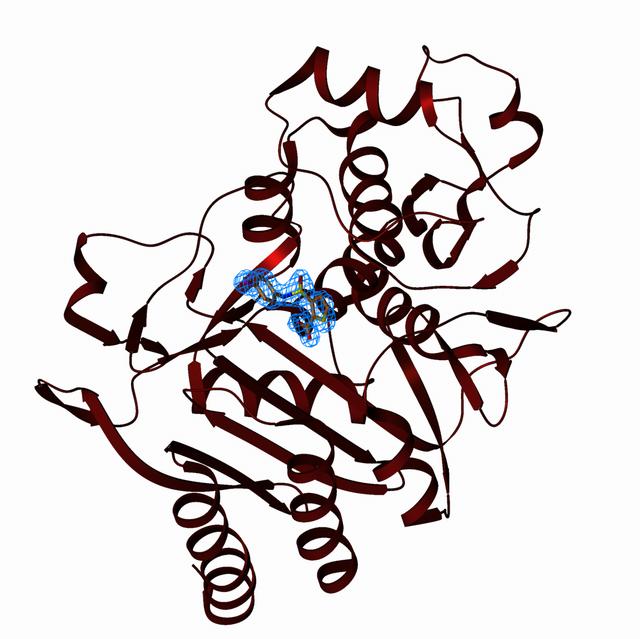
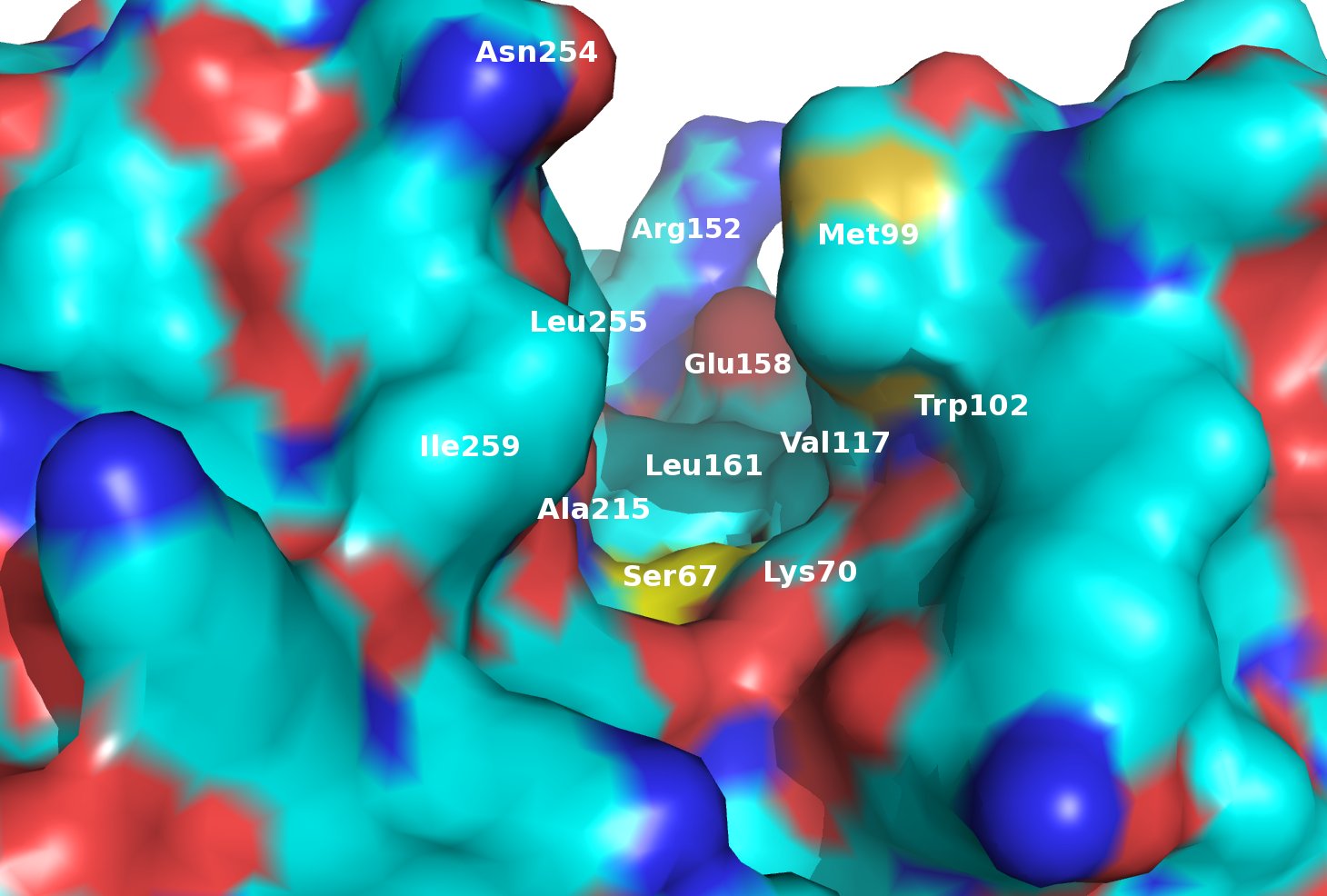
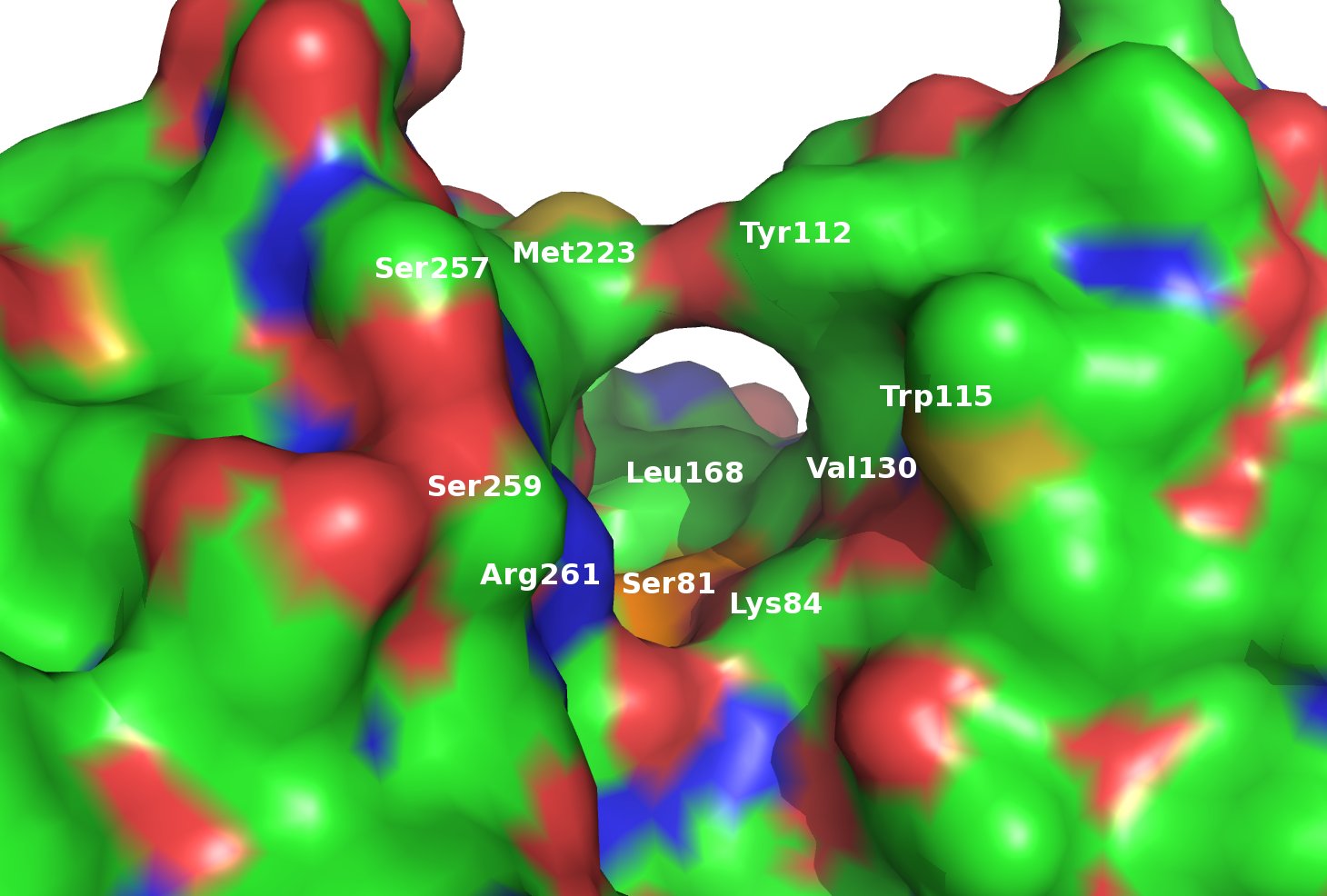
β-lactamases are the most widespread resistance mechanism to β-lactams and are categorized into four classes, each exhibiting a unique mechanism for destruction of β-lactam substrates. Of particular concern are the class D β-lactamases, which hydrolyze several of the most potent β-lactams in clinical use. In part, resistance derives from the structural similarity of the inhibitors to the β-lactams themselves. Therefore an urgent need exists for novel inhibitors that do not resemble β-lactams. Research in the Powers lab employs a structure-based approach to identify and characterize binding sites on the class D β-lactamases OXA-1 and OXA-24 and will be used to discover novel, non-β-lactam inhibitors for these key resistance enzymes using molecular docking.